The Different Types of Parylene Explained

Mallory McGuinness | June 5, 2020
Parylene is a chemical compound applied to substrates using chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Because Parylene coating deposits onto the surface molecule by molecule, it forms a defect and pinhole-free coating with excellent conformality. Parylene resists chemicals, can protect against caustic substances, acids, and corrosion, and more. Unlike conventional conformal coatings, Parylene is ultra-thin, providing superior coverage at 50% thickness. Its adaptability is enhanced by the fact that several types of Parylene coating exist, all suited for various industrial applications.
What’s the Difference Between Parylene Types?
The Parylene types covered in this guide are all characterized by different chemical compositions and physical properties. When using this substance and its numerous manifestations, you’ll notice that they all have different levels of permeability, dielectric strength, and other defining qualities. Choosing the best one depends on what application you’re using it for and what substrate you’re coating.
Here are several different types explained, including the best application use:
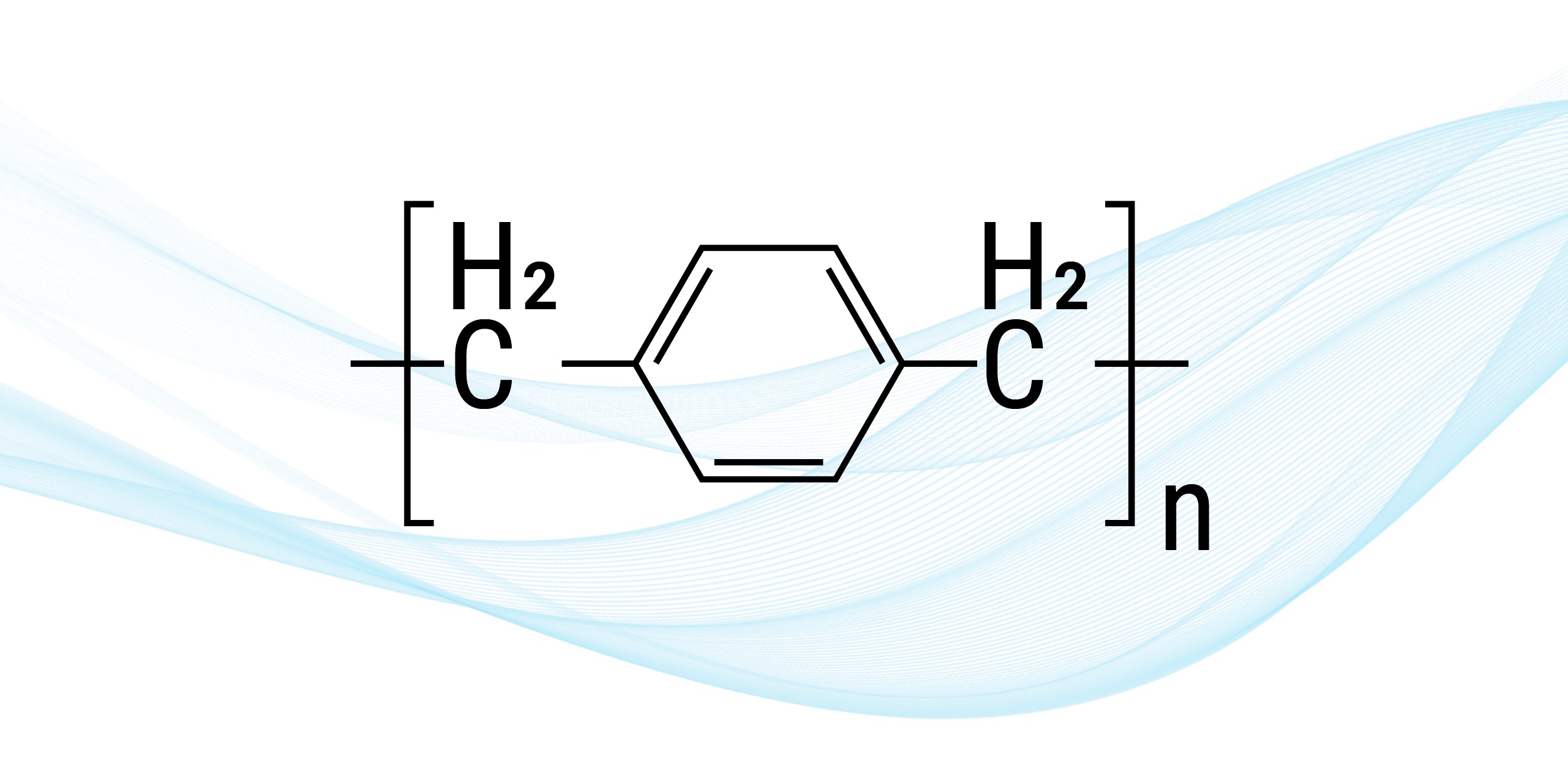
1. Parylene N
Parylene N consists of a linear carbon-hydrogen molecule structure. It’s the most fundamental, basic form of Parylene, which makes it suitable for devices that see high-frequency use. This type is distinguished by its vacuum stability and low dielectric constant. When going through the deposition process, Parylene N — along with Parylene C — has a higher deposition rate than many other types. This quality makes it convenient for commercial use, although it’s not quite as widespread as Parylene C.
Read more about Parylene N
Parylene N is also halogen-free. Halogens include elements like fluorine, bromine, and chlorine. This quality generally makes Parylene N preferable to Parylene C, as some industries require the Parylene coatings they employ to be halogen-free. For example, halogens in electronics can bio-accumulate within living beings, and they can be toxic to the environment when burned.
The most common applications for this Parylene coating include the following:
- Printed circuit boards: Most Parylene types protect the delicate inner workings of complex circuitry.
- Elastomers: Manufacturers use Parylene N to coat elastomers, polymers with weak molecular forces.
- Electronics: Most types of this material are excellent for protecting electronic devices, whether medical or non-medical.
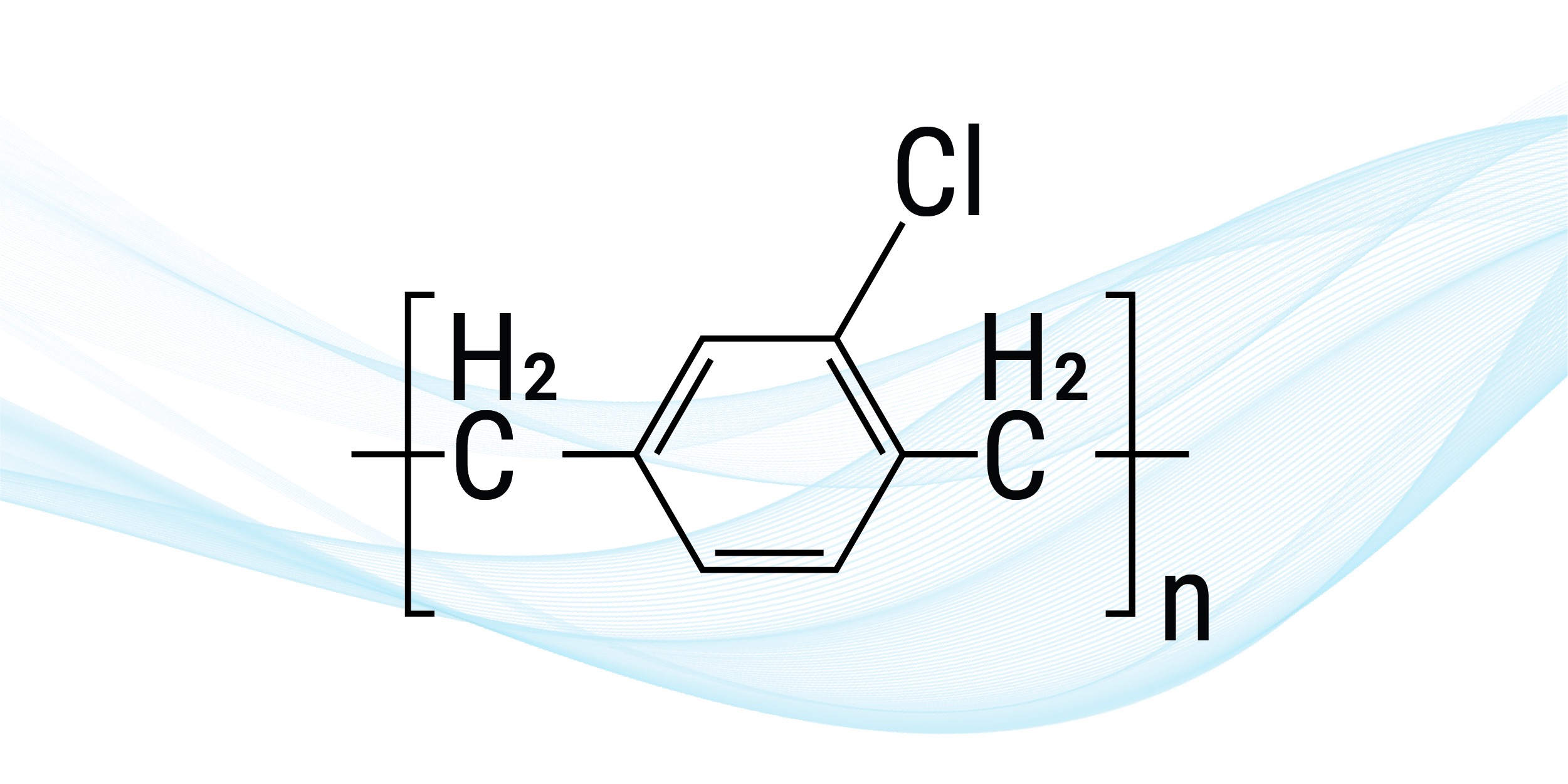
2. Parylene C
The moisture-resistant Parylene C is similar to Parylene N in that it contains a carbon-hydrogen molecule structure. However, for each molecule, it possesses one chlorine atom in place of a hydrogen atom. As a conformal coating, Parylene C provides a protective barrier for printed circuit boards. Parylene C also offers excellent protection against corrosive substances due to its low permeability.
Like other types, Parylene C is added to a substrate using the chemical vapor deposition process.
Learn more about why Parylene is used
If you have a device that needs high levels of protection, Parylene C is one of the best coatings available. Here’s where you’ll often see it being used:
- Medical Devices: Parylene C has been used in previous medical device studies as a substrate for peripheral nerve electrodes. A nerve electrode connects neurons to a brain-machine interface (BMI) and records nerve signals.
- Microelectromechanical systems devices (MEMs): Parylene C is often used to coat MEMs devices, though it can also serve as a structural or substrate material.
- Caustic environments: Devices that experience constant exposure to caustic substances fare better with a Parylene C coating because of the CVD process, which enables pinhole-free Parylene barriers.
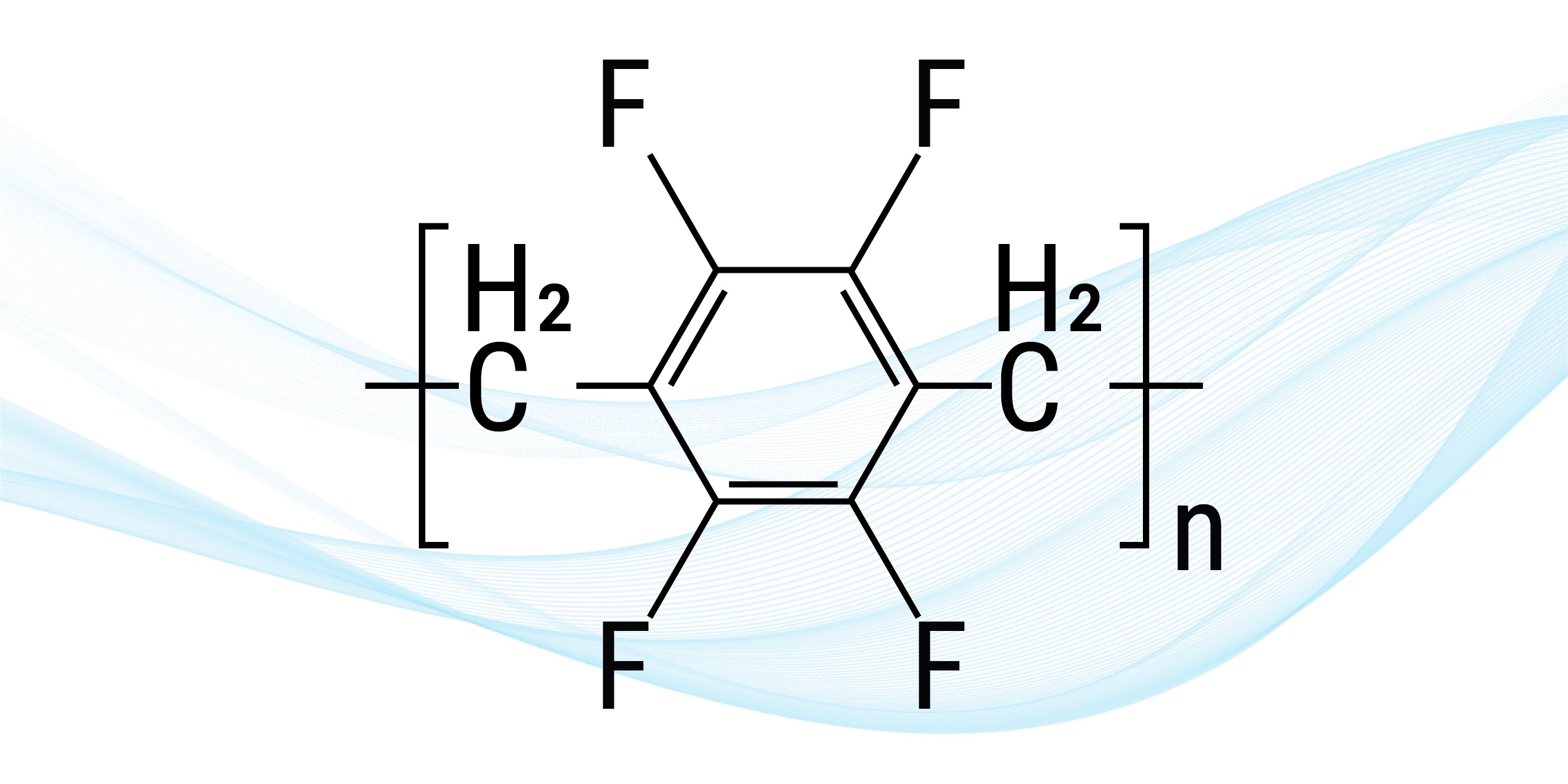
3. Parylene F (VT-4)
Parylene F doesn’t see the same commercial use as the other types on this list. However, it still possesses desirable qualities, such as a low dielectric constant and great thermal stability. It also allows for a higher coating density when used in various applications. This Parylene coating is characterized by its fluorination due to having fluorine atoms in its aromatic ring.
Although it’s not widespread yet, its properties can serve well for things such as:
- Field-effect transistors: One study showed that Parylene C and F were used within field-effect transistors to produce copolymer gate dielectrics. The study’s results showed that Parylene copolymer dielectrics offered stable and high-quality performance without the need for extra manufacturing steps.
- Microelectromechanical systems devices (MEMs): Like Parylene C, the F type also lends itself well to MEMS — especially those with high temperature requirements.
- Harsh conditions: Parylene F exhibits resistance to high temperatures and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Because of these properties, it could serve as a suitable substitute for Parylene C under harsh conditions.
Learn more about Parylene’s temperature range
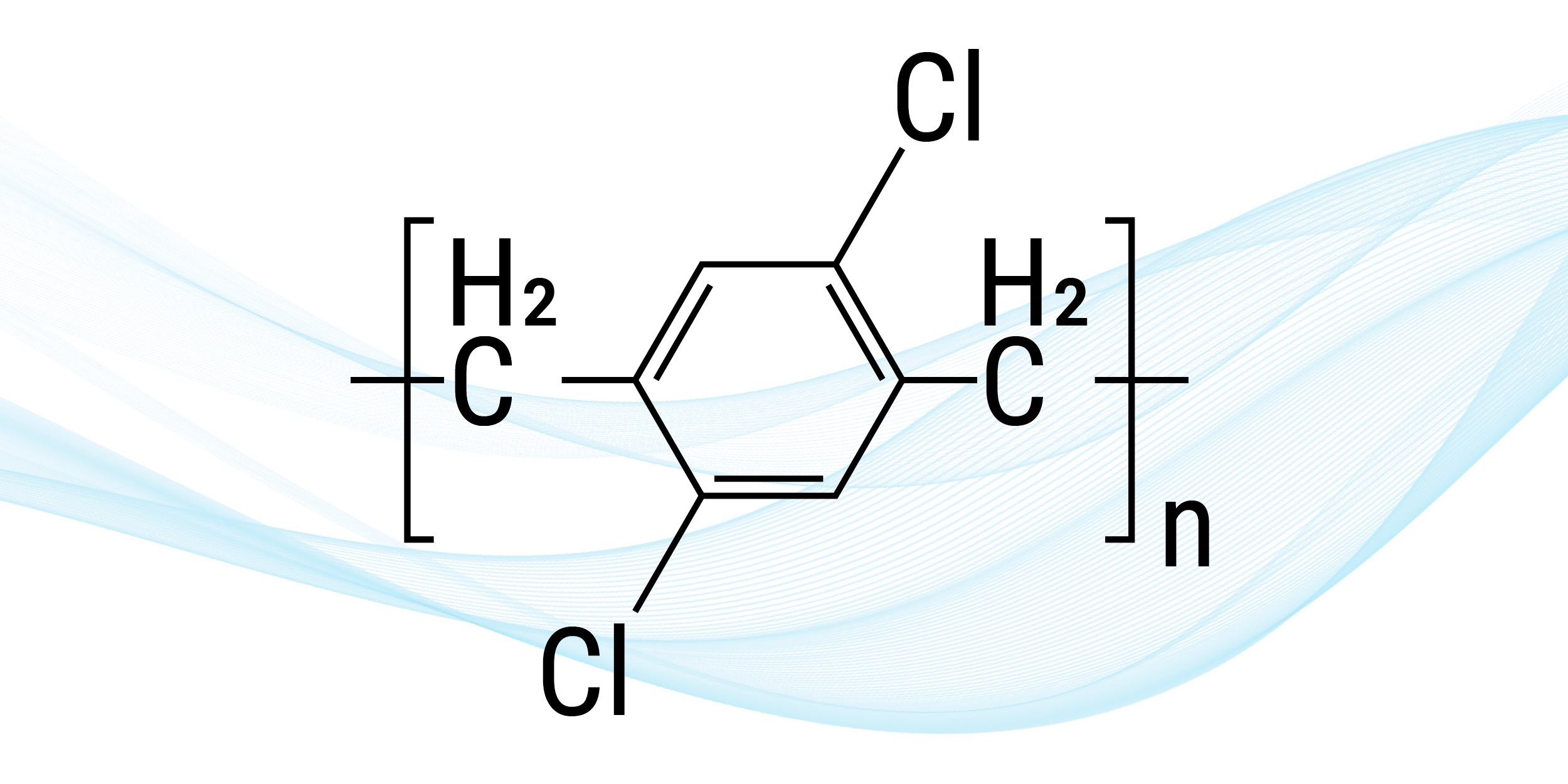
4. Parylene D
Parylene D resembles Parylene C in that it substitutes two hydrogen atoms for two chlorine. Both of these materials come from the same root monomer. Parylene D, however, lacks the same ease of use that C does — especially in terms of biocompatibility. It can hold up well when exposed to high temperatures, but it doesn’t work as effectively for coating things like medical devices.
However, it’s still suitable for other industrial uses. Some standard applications include:
- Aerospace components
- Electrical components
Learn about Parylene optical applications
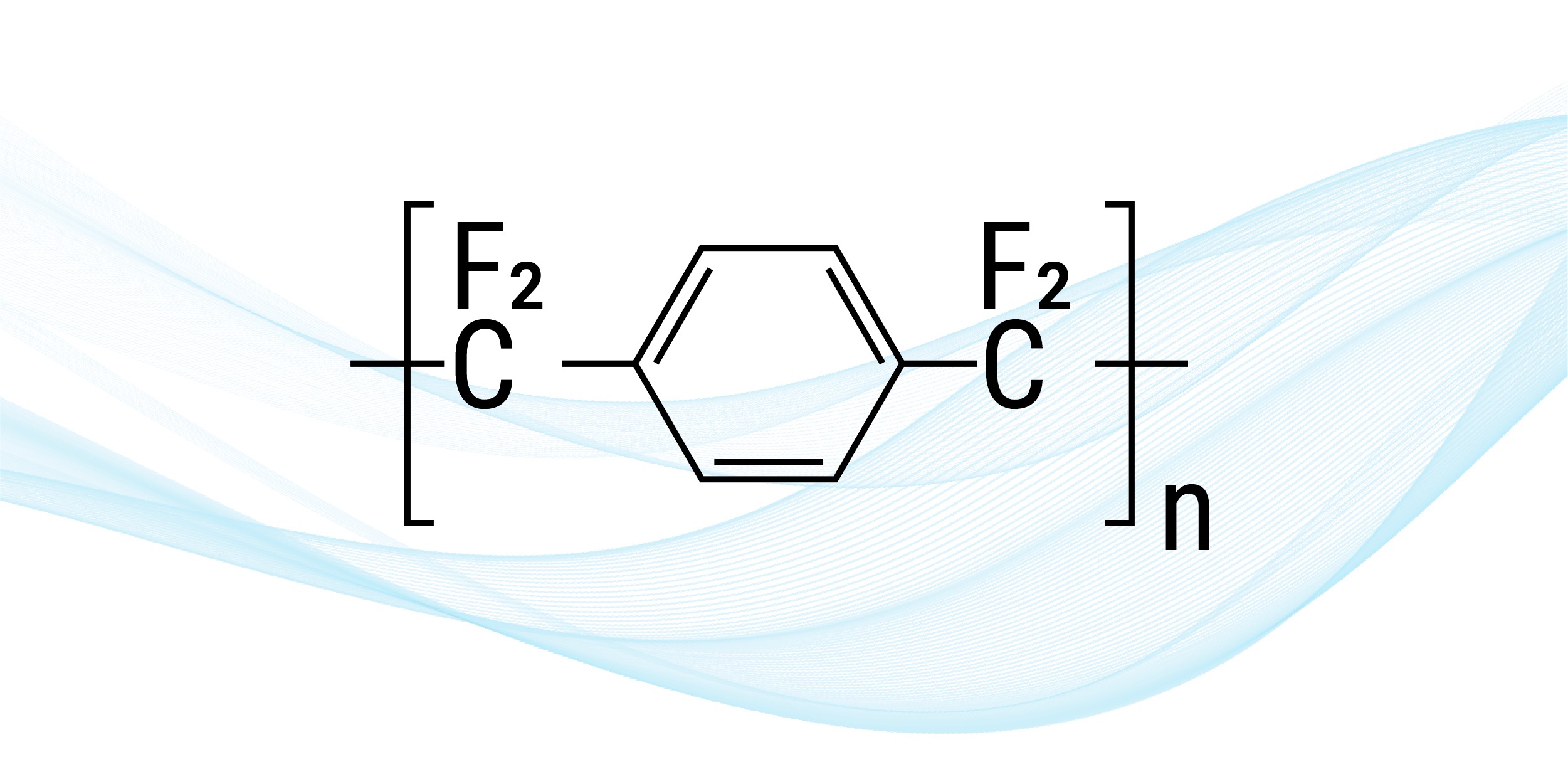
5. Parylene F (AF-4)
Parylene F (AF-4) possesses high oxidative resistance and UV stability. These properties make it fitting for specialized applications. It can withstand UV exposure without experiencing surface yellowing or degrading, which adds to its durability.
However, creating this conformal coating requires a three-step process. The additional stages increase production costs while limiting the yield, which is why it’s best to save this Parylene for only highly specialized uses. Some of these include:
- High-temperature applications
- UV radiation protection
Because the Parylene deposits onto the surface molecule by molecule, it offers a thorough coating with excellent adaptable properties.
Contact HZO for Parylene Conformal Coatings
Parylene is an excellent option for protecting electronic devices, but it isn’t the only choice available. Many types of coatings exist, with varying degrees of effectiveness and quality. If you’re interested in coating your devices, HZO can assist you. We serve a range of industries to help device manufacturers meet specifications, no matter the products produced.
Our turnkey solution helps us meet your coating needs by providing industry-leading, state-of-the-art Parylene coating equipment and employing proven material science. We have expertise in Parylene removal and industry-leading Parylene masking automation that reduces the price of Parylene coating services. Combining the entire package, HZO can offer you a high-quality experience with a durable finished product. Contact us today to speak with one of our highly qualified engineers about Parylene coating solutions.
Our turnkey solution helps us meet your coating needs by providing industry leading, state-of-the-art coating equipment and employing proven material science.
Mallory McGuinness

 Ryan Moore
Ryan Moore
Ryan is a 9-year veteran to the world of protecting electronics from harsh environments and a lover of all things technology.
Related
Discover how HZO can protect your product
